Arboretum
An arboretum is a collection of trees and shrubs. Primarily not native to our country, the so-called it has been a showcase for the diversity of woody plants since ancient times.
Plantings started according to plant families in the 1950s. Since woody plants are long-lived, the established planting patterns still determine their structure today. The area is currently undergoing a major transformation. New saplings are constantly added to old trees and shrubs. A dendrological educational trail is being developed, along which you will get to know the characteristic temperate woody plants of North America, China, Manchuria, Japan and the Mediterranean. A part of the educational trail is realized using plant material that can still be seen today.
Even in its current form, the arboretum hides a lot of value. The oak collection, which begins behind the rose garden, presents nearly 20 species from the native species in America and the Mediterranean regions, in addition to domestic species.
Special representatives of the nut family are a pine nuts, the Caucasian bird nut and the pecan. Among the hazelnuts, the rarity of our domestic forests is protected oriental candle worth highlighting. Among the birches with a special bark pattern, Daurian birch its old specimen has a striking appearance. With their arm-thick branches, they form impressive bushes that are decades old Tartar honeysuckle and ribbed honeysuckle. THE Japanese som its huge bushes are conspicuous during their deciduous flowering.

The butterfly family is also represented by many species. Their inflorescences and pods vary in color and shape. THE Judean trees they produce their flowers and fruits on the thicker branches and trunk. Their flowers open in the spring even before the leaves emerge. THE pie trees they bear huge thorns on their trunks and branches. Dioecious plants, only fertile individuals develop large, 20-30 cm huge pods.

The collection of maples shines brightly in autumn. In this case, the tartar maple, the triple maple, the red maple its foliage displays all shades of red.
Members of the rose family are a beads, the shoulder blades, that is Apple- and plums, the hawthorns and the wild roses.
The real surprise of autumn is the Chinese elm, which a with amber flourishes together during this period.
The arboretum also includes the collection of open crops.
Annual collection
In many parts of the garden, annual plants can be seen in colorful, abundantly blooming beds, which decorate from the beginning of summer until the autumn period. Most of them come from tropical, subtropical and Mediterranean areas. In their homeland, they are often perennial, but due to their sensitivity to frost, they only live for one year here. Most of them are sun worshippers, but there are some that also grow nicely in semi-shaded and shady places. Many plants bear the traces of breeding, and there are countless varieties with fanciful names. The number of species and varieties presented varies from year to year, and there are more than a hundred of them.
Their main adornment is the flower or inflorescence. The tall one Cleopatra's Needle its elegant appearance is given by the multitude of long stamens extending from the flowers. The needle-like appearance of its fruits is also very spectacular.

THE winged ornamental tobacco its flowers are fragrant at night. THE Torrenia and the dwarf lobelia due to their smaller stature, creeping foliage and profuse blooming blue flowers, they look good in the border of the bed. Belonging to those with nesting flowers copper flowers, coneflowers, garden butterfly flower or just the stinky blue many varieties are also popular ornamental plants in small gardens.

Other indispensable members of your annual flower procession are the scarlet sage and the garden petunias, the garden begonias, the nebanc flowers and the dahlias various versions.
Decorative leafy plants provide the defining color spots of the beds. Among them are the ones that form huge, colorful bushes flower nettlesnearly 30 varieties are visible.

Living fossils
The name living fossil comes from Darwin. Only a few dozen open-growing species can be classified among them, those that have existed in an unchanged form for more than 100 million years. They lived their heyday at the same time as the dinosaurs, in the Middle Ages. For a long time, they were only known as fossils, they were thought to be extinct. Their living individuals have only recently been discovered. They survived in isolated habitats and often only a few hundred individuals make up their world population. They are on the verge of extinction and deserve increased attention and protection.
Among them the Szechuan old pine is most closely related to the history of the garden. Living specimens of the species were discovered in 1941 in China, in the province of Sichuan. Through a seed exchange relationship, the seeds from which the three oldest trees that can still be seen around the greenhouses were grown from here.
It is native to California mountain mammoth pines they are the heaviest living creatures on Earth, their weight including the root system is estimated at 6,000 tons. Several specimens of them can be seen in the Botanical Garden, the oldest of which is only a baby at the age of 60. Their leaves are scaly, their brown bark is soft and spongy.
THE coastal mammoth pine its needles, on the other hand, are comb-like, flat, and soft. Young specimens can be seen in front of the Mediterranean house and in the open-air collection, and in addition to the basic species, there is also a blue version.
THE fern fir its natural population was discovered in China at the beginning of the twentieth century. Its fan-shaped leaves have a medicinal effect, they turn yellow in autumn and then fall. The fleshy seed coat becomes unpleasant-smelling during ripening, but its seeds are edible. He deserved the name "Tree of Hope" and proved to be a true survivor; six ferns survived even after the Hiroshima atomic bomb. It has now become a common urban tree.
It is related to the house pine Chilean Araucaria native to the Andes. Its distinctive triangular, pointed scale leaves are arranged in a spiral line on its trunk and branches. It can be seen next to the greenhouse.

THE Wollem pinewas only discovered in 1994. In Australia, in one of the hidden gorges of the Wollemi National Park, a few hundred individuals survived.
A perennial collection
Perennial plants live and decorate the same place for several years. There are several bred versions marked with variety names. The presentation serves a dual purpose, as a collection it introduces popular species and varieties, but at the same time, aesthetics and enjoyment were also an important aspect during its design.
The perennial beds are attractive from spring to autumn, thanks to the plants that bloom in different seasons. Herbaceous perennials can be planted together with annuals and smaller shrubs in various beds.
The tall, powerful species not only decorate with their flowers, but the lower plants also stand out beautifully, forming a green wall in the foreground of their uniform foliage. The smaller one yarrow tail the leaves of species and varieties are finely serrated, their tent-like nest inflorescences form colorful spots.
Popular plants for plantings are lips. Among them, they stand out with their stature Asia Minor cat's testicle species. They liked the fragrant ones sages also, their brightly colored flowers are grouped at the top of the shoots, but we also enrich the composition with other species. With its woolly hairy leaves, it creates striking, silvery spots bunny ears. THE gamandor, the lizard grass and that tendrils of tendrils its stems can be used as a border plant.

THE necklace with garlands its special appearance is due to its spicy leaves and candle-like flowers. It stands out from me like a burning torch comet torch lily also its flowers. In autumn, they form bright spots of color asters his bushes.
Grasses and sedges decorate with their stems and leaves of different colors and patterns and are also important in dividing the bed.
Spice and herb garden
The structure of the Spice and Herb Garden evokes the atmosphere of former monastery gardens.

More than two hundred species of the collection can be seen planted in plots. Plants that affect the same organ system, for example, the nervous system, the immune system, the circulation, the urinary tract, the digestive system, were placed in one bed.
In the list below, we highlight plants found in the collection that have been proven by research to have a medicinal effect.
Among the species affecting the nervous system a Catnip, the hops, that is St. John's wort it is a common ingredient in soothing tea blends. It has an important immune system strengthening effect purple marigold and the Chinese creeping magnolia. The regeneration of skin and mucous membrane injuries is proven to be helped by marigold, the burdock, that is arnica and the black night light. It effectively soothes a cough medical ziliz, that is medical fenugreek, the coltsfoot and the spear plantain application.
The richest part of the presentation species is the group of plants that affect digestion. The anise and that fennel helps with bloating. THE benedict grass and that wild ginger root an important raw material for Swedish drops and bitter liqueurs. THE milk thistle silymarin extracted from its seeds is a component of liver protective preparations. Herbs are plants that also affect digestion, which give our food a decisive taste even in small quantities. THE laurel, the dill, the rosemary and the coriander belongs here.

Plants that are directly dangerous to the body, causing poisoning and even death can be seen in two fenced plots. Some of them are used as medicinal plants and provide raw materials for medicines. However, their domestic use is strictly prohibited. This includes the red foxglove, the may lily of the valley, that is autumn circle, the spotted hemlock, the nightshade and the maddening entrails. It was considered a magical plant for witches mandrake can also be seen among poisonous plants.
Trees and shrubs with medicinal effects were placed around the plots. Representatives of sea thorn, the goji, the mountain eucalyptus, the Chinese barberry, the meaty catfish, the elderberry or just the friend bush.

The herb garden includes French and English lavender a lavender plantation created from many horticultural varieties and an exhibition showing the many uses of lavender.
Japanese garden
The large Japanese garden includes the lotus pond and the area starting with the Japanese gate, interwoven with streams and paths. In terms of style, it can be divided into two parts.
The first unit is the lotus lake and its surroundings, modeled after the so-called paradise gardens. He is revered as a saint in the East lotuses symbols of purification, and the islands of the lake symbolize the world of eternal life in paradise. There is a stone lantern on the "turtle island". The narrow strip of the "crane island" stretches at the back of the lake and leads through a wooded area.

The largest island of the lotus pond is the "waterfall island", which also presents the style of Japanese tea gardens as a separate unit. The tea garden and the waterfall are designed to promote quiet contemplation. THE yew treeswith fir treescomes and swamp cypressesat the highest point of the shady environment covered with fuji dana. This purple acaciareason with a five-leafed acebia and with Japanese creeping hydrangea cozy rest area also offers a perfect view of the lake.
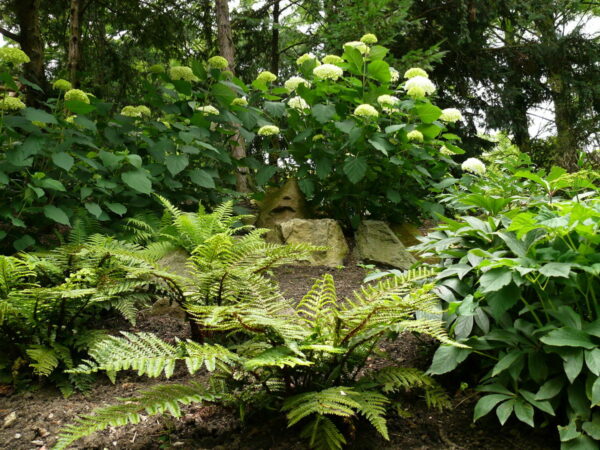

Shade-tolerant plants, a Japanese Chubby, the pearl lawn lily and the flat-stemmed snakebeard covered by a thick carpet. The bearer of huge inflorescences hydrangeas and the lush foliage ostrich ferns its ensemble sometimes creates a real wild novel environment. The defining plants of the autumn period are the colorful foliage finger mapleok, that's when the Japanese anemone too.

The second large unit of the Japanese garden is characterized by islands divided by streams. You can enter the garden through the red Tori gate, which is a traditional Shinto symbol, symbolizing the passage between the material and spiritual worlds.
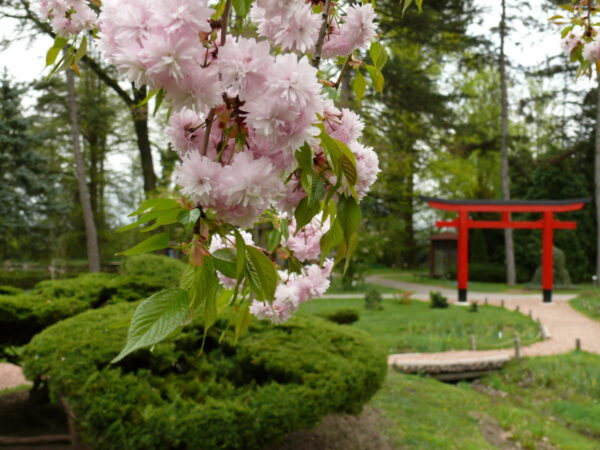

The walking path is accompanied by Japanese lanterns and shaped trees made of evergreens. First in the spring Japanese apricot, then a Japanese decorative cherries different varieties open their pink flowers. Other characteristic species are a Japanese honeysuckle, the Japanese laurel, the holy tree, the Japanese sickle pine, the Japanese Scots pine. The bamboo collection of nearly 40 species can also be found here.
Cactus and succulent house
In the cactus and succulent house, we can get to know the drought-tolerant flora of deserts, semi-deserts, and rocky grasslands. The collection, which presents more than 500 species, consists of two parts.
Smaller plants were placed in the gallery room opening from the tropical greenhouse. Larger plants can be seen in the neighboring Mediterranean greenhouse. Most of the latter were put in place at the end of the 1970s and have been developing there ever since.

The body structure of succulent plants is extremely adapted to the extreme growing conditions. The leaves of many species are thick, leathery, often waxy or covered with hairs.
In the case of cacti species native to America, which make up the largest part of the succulent collection, the leaves have been almost completely reduced, turned into prickly thorns, and are able to store water in the tissues of their stems.
THE fig cacti between 60-70 years old, tree-shaped specimens can also be seen. Their fruits are popular fruits. Flat, leaf-like stem members of plants carry out photosynthesis. At the end of the stems, the flowers are lined up like toes, followed by the fruits, which is why they are also called bear's foot cactus. The columnar cacti its candelabra-like shoots reaching the sky almost reach the roof of the greenhouse.
It sounds similar to cacti dog milks, represent the flora of the deserts of Africa. Just like the gravel plants, whose shoots have been reduced to a single pair of fleshy leaves and the plant lives hiding in the sand, disguised as gravel.

The aloes its homeland is also Africa, among the many species presented, the best known is the medical aloe, which is also cultivated as a medicinal plant, the leaves of which are processed.
Nowadays, it is widespread in Mediterranean landscapes agaves They come from South and Central America. 40-50 year old specimens of American agaves are real specialties. They are characterized by the fact that they bloom once during their lifetime, develop a 6-7 meter tall flowering axis, and then die after fruit ripening. In recent years, we have been able to admire the flowering of several specimens.

Succulent plants include geraniums, the coral flowers, the wax flowers, the carrion flowers and the crystal flowers, which are also popular ornamental plants.
A collection of cultivated plants
In the collection of cultivated plants, we present useful plants that serve humanity well. Those special species and varieties that are less common in domestic small gardens and cultivation, however, play a significant role in the world. The plants can be seen arranged in plots in the yard surrounded by the fence. Most of them are frost-sensitive, so every year we assemble the collection of nearly 120 species by sowing seeds and planting seedlings, which will always be unique.
Food crops play an important role in human nutrition. Among them, we present quite a few exotic species, which are grown on huge plantations in tropical and subtropical areas. Tuberous plants are an important source of starch. Such plays a significant role in the tropics manioc, the reservoir, the sweet potato and the real one yam root. Another possible source of starch is fruit. The special cereal crops of the presentation are a Job's tears, the annual teosinte.
In the case of certain plants, the leaves are edible. It is a lesser-known leafy vegetable in our country precious pearl, the Malabar Spinach, that is New Zealand spinach.

The unripe fruit is used a chamois horn and that reason case, that is at artichokes and the bud flower is on the menu. The row of exotic edible plants is colored by the one used in rum production sugar cane.
The edible and industrial oil plants can be seen in two separate beds. Vegetable oils and fats can be extracted from the seeds. The well-known species are the special plants of the presentation. That's how it is oil palm, olive tree, the castor oil, the sesame, the peanuts.

The next group of crops are fiber plants. Plant fibers can be provided by seeds, leaves and stems. They are used to make many useful items, such as canvases, textiles, ropes, laces, insoles and paper. In the bed a flax, the hemp and plant species grown on an industrial scale in the tropics, a jute, the banana fiber, the sisal and the cotton can be known. THE sponges in this case, fruit fiber is used, which is also suitable for making sponges, towels, insoles and filters.

Before the appearance of synthetic dyes, dyeing plants provided dyes for dyeing various textiles and materials, coloring food or making ink suitable for writing. It had a special use lamb roastnak, its root was used by shepherds to mark their sheep. The traditional plants of the presentation suitable for home use are: pitch grass, the marigold, that is golden rod, the nettle, the painter's pipe, the ordinary tobacco, the elderberry. In addition to them, there are two painting plants that once played a significant role on an industrial scale indigo and his famous rival a painter's sink is also visible. The leaves and stems of both plants can be used to produce the blue dye. An exhibition is also connected to the presentation of ornamental plants.
Lotus pond
One of the most spectacular and oldest parts of the Botanical Garden is the lotus pond. Medre was excavated in 1931. Its namesake plant was installed a year later. The Indian lotusIstván Győrffy, the first director of the garden, came across it at the ornamental lake of the Návay Castle in Óföldeák. Virginia swamp cypress trees grow on the shore of the lake, and around their trunks a multitude of breathing roots emerge. Their coniferous leaves are soft, turn red in autumn and fall off. On the lakeside peat fern and giant horseradish also has an extensive population. Among the native and protected aquatic plants in our country, white fairy rose can also be observed. Although the lake and its flora are valuable in themselves, they are also an important part of the Japanese garden.

The beautiful Indian lotus, native to the subtropical regions of Asia, is a seasonal decoration of the lake. It spends the winter dormant in the mud, and sprouts from its underground stem every spring. First the leaves appear on the surface of the water, then as the weather warms up, flower buds appear in increasing numbers in June. During its peak flowering period, in July and August, the lake is covered with a carpet of green leaves and an abundance of dark pink flowers that stand out from it. Its fruits develop in fruit holders similar to those of a shower rose, which become woody in the fall. Its seeds retain their ability to germinate for up to 1,000 years.

The survival of the Indian lotus here in the botanical garden is ensured by special environmental conditions. Near the bottom of the lake, thermal water at 22°C flows continuously throughout the year, so the plant can overwinter in the mud without damage.
At the Lotus Days event, traditionally held on the last weekend of July, we draw attention to the multifaceted role of the plant. It is also an important food plant, ornamental plant and spiritual symbol in the Far East, and its motif is echoed in art and architecture. It is also connected to modern technologies, the phenomenon of the lotus effect - which is the perfect self-cleaning and water-repellent ability of surfaces - was discovered during the examination of lotus leaves.
Bird-friendly garden and animal protection
Our herb garden has a strong tradition of observing and protecting birds. As a member of the Hungarian Ornithological Association, Marián Miklós has been making ornithological observations here since the 1970s. In addition to the diorama showing the bird life of the Botanical Gardens, his memory is preserved by a statue made by the sculptor Márton Simor.
In the bird-friendly garden, we can get to know the trees and shrubs that are ideal feeding, nesting and hiding places for birds and the many useful animals living in the garden. We present the practices, types of birdhouses, the frog bunker, the hedgehog house, the bat house and the peleod house, with which we can successfully lure animals into our garden.

The Botanical Garden, although artificially created, can still be considered a natural habitat, where many animals find their living conditions. A visitor who walks quietly and with his eyes open can see real rarities during his walk. The white stork has been nesting on an old chimney for several decades. Common inhabitants of lakes and canals are terrapins and water slides. Wood frogs and toads signal their presence with their loud croaking. The insect world is extremely species-rich thanks to the diverse habitats. Aquatic, waterside, meadow, desert and forest species can also be observed. They can be seen here stag beetle species, a great hero villain, the dragonfly species, among butterflies a sword moth, the swallowtail butterfly too. Perhaps it is surprising, but it is seen regularly bakcó and Grey Heron, that is long-eared owl and the barn owl also nests in the area. More than fifty artificial burrows placed in trees help the nesting birds to settle down.
Mammals can be seen less often, but with red squirrel, with hazelnut flakes and with a wood mouse we can also meet, a bats are also represented by several species.
Mediterranean and subtropical greenhouse
The Mediterranean greenhouse is a showcase for non- or only moderately frost-tolerant plants. Most of the woody plants have been growing here for decades, most of them would have outgrown the building long ago without the annual trimming of the foliage. In the summer, the potted plants are taken out of the greenhouse. The large-sized plants of the succulent collection, cacti, agaves and aloes, can also be seen here, some of which have now become typical plants of the Mediterranean areas.
Most of the 180 species that make up the collection can also be found around the Mediterranean Sea. The olive tree, the laurel, the oleander, the myrtle, and the capers indispensable members of the Mediterranean landscape. Common species a carob tree also, whose pods with a high sugar content are used to make the carob powder that replaces chocolate. Palms with huge leaves standing in cauldrons at the top of the trunk are also typical, for example the date palms and fan palms population group.
Known species of citrus fruits, a Mandarin, the orange and the citron in addition to older specimens, it is a real specialty giant lemon obsession cedar, the kaffir lime, and the kumquat. Most species bloom regularly and produce fruit.
It's a real sensation every year silver acacia flowering. The bright yellow flowers, clustered in heads, bloom in winter.

It can be seen near the main entrance horsetail cassowary tree its leaves resemble the plumage of a cassowary.
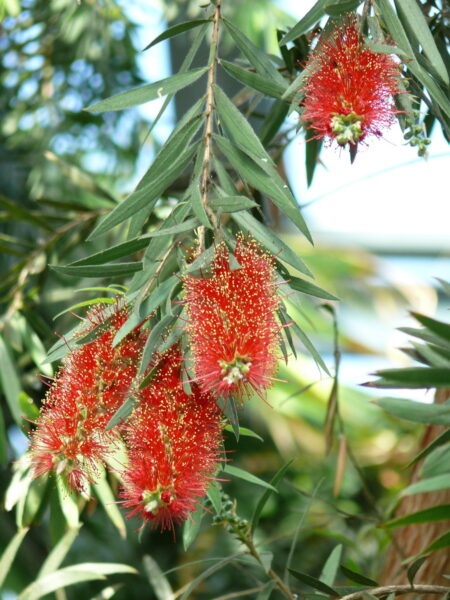
THE brush flower its name is also telling, its flowers resemble a glass washing brush. It is native to the southern hemisphere Araucaria several wood-sized specimens are also visible. It is of Asian origin sarcophagus tree its interesting feature is that its wood provides excellent coffin material. THE loquat its fruits ripen at the end of winter and have a pleasant taste.

It is decorative with its colorful leaves gravel cluster it shines in several color variations when run on pergolas.
Many species of Mediterranean plants, a oleander, the pomegranate, the silk myrtle, the Chinese hemp palm and the evergreen magnolia it can also be seen planted outdoors.

Open source collection
In the Füvészkert, you can find many evergreens throughout the garden, but in 2005 we created a separate open collection. We have been expanding this since then, and it is now suitable for presenting nearly 40 species and varieties.
The open fruits have a characteristic structure, and at first glance they differ in many ways from other woody plants. Their leaves are reduced, in needles or scale-like leaves. Most of their species are evergreen, that is, their leaves do not fall all at once with the approach of winter, but gradually. Stamen flowers make up the panicle, fertile flowers make up the cone inflorescence. They have no fruit, so the cone is actually a woody inflorescence. THE junipers its spherical cones are called pine cones. THE yew trees and the fern fir in the case of the seeds are protected by a fleshy seed coat similar to the fruit. Almost all parts of the plants contain resin ducts, from which the resin with a characteristic smell comes to the surface and closes the wound.

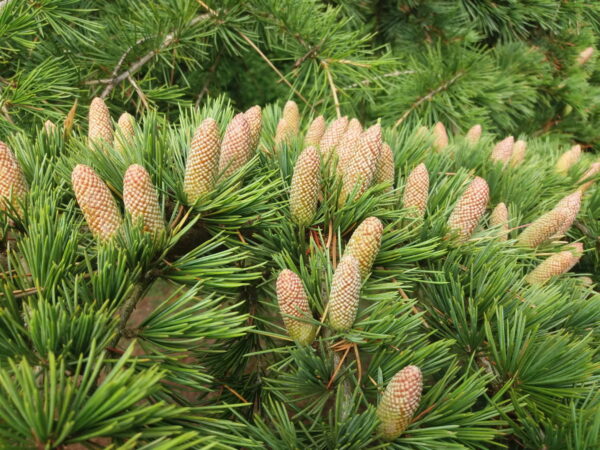
Walking around the collection, you can get to know the fir trees, spruce trees, silk pines, cedars its most characteristic representatives. Such is the deciduous tree Szechuan old pine and the common larch, considered giants of the flora mountain and coastal mammoth pine young specimens, native to the high mountains mountain pine, as well as thousands of years, the real Methuselah age Scots pine with resinous needles. The horticultural versions of junipers, thuja and cypress with different leaf shapes, color variations and growth characteristics can be seen in the semicircle around the rose garden.

Orchid house
In the orchid house, you can see tropical orchids that like warm and warm-temperate house conditions. The collection is most spectacular in the winter, when most plants are in bloom. The flowers are very durable, they stay fresh for up to 1-2 months, and are often fragrant.

There are more than 30,000 known species of orchids. They are present with the greatest species richness in the tropics, where they primarily lead a tree-dwelling lifestyle.
Their body structure and lifestyle are very special in many ways. Their seeds are tiny, so-called dust seeds, and their germination requires the presence of a fungal partner. Many species develop aerial roots with which they cling, photosynthesize, and utilize the vapor in the air. They can store nutrients in their fleshy, thick leaves, stem tubers, and thick roots. Their flowers are often large, have a special color, and their shape can also imitate insects. One of their six sheaths has been transformed into a so-called honeycomb, which is an ideal landing strip for pollinating insects.
In the last century, orchid hunters still visited the rainforests, but thanks to breeding, today some varieties have become easily available houseplants. However, keeping true rarities, naturally occurring botanical species, requires real expertise. The collection currently presents more than 100 species and 50 hybrids of 57 genera.
Among the soil-dwelling orchids, you can find a venus slipper (Papiopedilum) species and hybrids. It has a creeping stem rooted in the ground vanilla the only orchid whose fruit is used as a spice.
THE butterfly orchids (Phalenopsis) are well-known ornamental plants. Our collection includes the smallest and largest species of the genus, as well as many botanical species.
The well-developed stem tubercles are easy to recognize moving lip orchids (Bulbophyllum) genus members.

Also called the queen of orchids bugako wines they are very popular among collectors because of their particularly beautiful flowers. THE vandals they can grow up to 2-3 meters.
In addition to representatives of the larger orchid groups, the collection is pansy orchids (Miltonia), it jewel orchids (Ludisia), a butterfly wines (Oncidium) and several species of genera that do not even have Hungarian names.

In summer, it can be seen outdoors in hanging baskets oxhead orchids (Stanhopea) several species. The blooming plants are indicated from afar by the pleasant scent of vanilla in the air.
Fern house
In the foyer of the butterfly house, you can get to know the representatives of ferns and lacewings that live in the tropics. The collection presents more than 70 species and varieties of plants belonging to the harstas and bearing many ancient marks in their body structure. Their roots are less developed, and their stems often crawl under the ground like roots. Their leaves not only carry out photosynthesis, but also carry asexual reproduction formulas, spores. The spores develop in spore receptacles on the backs of the leaves, forming interesting patterns. The young leaves of the ferns curl up like a shepherd's staff and hide in the foliage.

THE for indoor ferns they have really typical fern leaves, they are long, narrow, composed of many leaflets, and winged. Spores are hidden by circular spore holders on the backs of the leaves.
THE venus frills its foliage is dense, its leaves sit on a thin but pronounced blackish-purple petiole. Their spore holders are arranged in a dotted or continuous line on the edge of the leaf.

With its huge stature and nearly 1 meter long bright green leaves bird's nest fern the most spectacular member of the collection. Its base is surrounded by dried leaves like a nest. It lives on a tree, just like the staghorn fern. The latter also serves as a good example of the phenomenon of bipedalism. The spore-bearing leaves of the plant are shaped like the antlers of a fallow deer, and its base is surrounded by cup-shaped humus-collecting leaves like a flower pot.
It's a real specialty viviparous frill, on the leaves of which small plants capable of rooting develop.
The licorice ferns as their name suggests, their rhizomes are sweet-tasting, creeping, and densely hairy.
THE lace tapestry the shoots of its representatives form carpet-like colonies, their leaves are scale-like.

There are also many horticultural versions of ferns and laceworts, the more undemanding, drought-tolerant species and varieties are popular foliage plants.
Systematic collection
University herb gardens also play an important role in education. The thematic taxonomic collection created in the 1950s to aid education serves this purpose. The presentation, which has been revised several times over the past decades, took its current form in 2021.

The six raised beds laid with bricks look inviting from afar. A brief summary of the history of the organization can be read on the unique ceramic decorated wall. The work of Carl Linnaeus and Charles Darwin created the scientific foundations of systematization, for the clarification of which molecular methods are now used.
The taxonomic collection was also divided based on the results of the latest genetic tests.
Species of closely related families were placed in each plot. We mainly present the herbaceous species of the domestic native flora. Some of the plants come from our own collection, but many species also came through the seed exchange relationships between the botanical gardens. Representatives of nearly sixty families can be seen, dicotyledons can be seen in five beds and monocotyledons in one bed. There are more than 250 species of dicotyledons and nearly 80 species of monocotyledons. This number changes slightly from year to year, the collection is enriched with new species and also loses species.

It is represented by a very high number of species buttercups, the carnations, that is lips, the they are nested, the roses and the female petals his family. Most of the plants are perennial, but some characteristic annual species can also be found. They include the soot, the cornflower, the poppy and the maddening entrails. The collection is also enriched by many protected species. In addition to the special, rare species, the representatives of the species occurring on the road, a testes, the nettle, that is plantains and many other common plants can be found in the plots.
A collection of insect-catching plants
On the upper floor of the tropical greenhouse is a collection of insect-catching plants. It is characteristic of these plants living in nutrient-poor habitats that they supplement their nitrogen and phosphorus needs from animal sources, by capturing and digesting animals.
In order to lure and capture their prey, they use a variety of methods, but in all cases the leaf acts as a trap.

The most important genera in our collection are - a cornflowers, the jugs, the venus fly swatter, the dew grasses and the rences – representatives and some real rarities, that is Australian jug, the cobra lily and the Guyanese sun jar we present, which show 75 species and varieties.
We ask our dear visitors not to touch the plants so that these special plants can develop undisturbed!

The best-known "carnivorous plant" is a venus fly swatter, whose leaf trap, which can be folded like a book, is activated when the victim touches several sensor hairs at the same time. However, each trap can only be folded a few times, after which it dries up.
THE weight gainers its traps work like sticky fly paper. Their rosy leaves are thick and densely covered with glandular hairs. An insect that strays onto the surface of a leaf easily gets stuck in it.
THE dew grasses they secrete a spectacular, dewdrop-like and sticky secretion on the surface of the leaf, which is an attractive target for thirsty insects.

Native to the tropics, it has a creeping stem jugs they have a hanging jug-shaped stack trap. The victim easily slips inside the trap, and the hairs on the wall of the pitcher guide it further into the depths of the pitcher, until it finally ends up in the liquid containing the digestive enzymes.
It is native to North America cornflowers its traps work in a similar way, at ground level. Their traps are in the shape of a hunting horn, brightly colored, and sometimes transparent, which is very attractive to insects.
THE rences have the most complex trap type. Their bladder traps work on the vacuum principle, the trap door opens when touched and the victim is sucked into the bag.
Catching insects is only a supplemental way of nutrition for plants, and they photosynthesize just like any other plant and survive even if they are deprived of prey for long periods of time.
Due to their special structure and decorative flowers, some species have also become popular ornamental plants. Thanks to breeding, there are now many color and shape variations.
Rose garden
The rose garden, or rosarium, has been located in the central location of the Botanical Garden for more than 70 years. The circular area is marked by paths decorated with a wrought iron pergola system, which lead to the central rose hut. More than 300 species and varieties of roses, nearly 3000 stems, can be seen in the collection. In the beds, the names of the individual varieties are indicated by signs.

Breeding roses has been going on for thousands of years. The wild roses - they include the wild rose, the rose of woe, the Chinese rose, the hundred leaf rose – and by crossing other species, hundreds of thousands of rose varieties have been created today.

During breeding, the goal is to increase the beauty of the flower, to create varieties with increasingly larger flowers, more petals, and more and more special shapes and flower colors. In the case of some varieties, the enhancement of the scent is essential.
Our country also occupies a prominent place in the field of rose breeding. More than 40 varieties of so-called Márk roses bred by Gergely Márk can be seen in the collection. Among the great breeders of the world, Meiland, Kordes, Tantau, David Austin, Poulsen, Lammerts and others also decorate the garden.
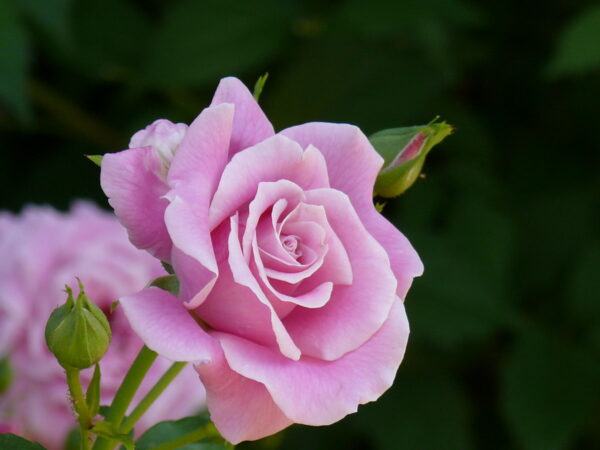

There are already many roses with growth characteristics: tea roses that produce beautiful cut flowers, baby roses that grow many roses at the end of the branches, creeping and runner roses, miniature roses and park roses. In addition to these, you can also see representatives of today's popular stock roses.

The continuation of the rose garden is the collection of historical roses established in 2015. Walking towards the arboretum, you can see their tall bushes on both sides of the road. More than 40 varieties of them can be seen. They are most spectacular when they bloom, at the end of May and June. Their fragrant flowers are mainly in shades of pink and red.

Among them are those that exude a resinous scent Moss roses, is capable of repeated flowering Portland roses, forming huge bushes, abundant in rose oil Damascus roses, with white or pink flowers Alba roses and the many-petalled, rich in fragrances Centifolia roses. Some types of rosehips also decorate in autumn.
Rock garden
The landscape-type rock garden rises behind the fairy rose lake.
It is home to nearly 400 plant species and varieties. It shows its most beautiful face in spring, when the flowers blooming in different colors bloom like colorful spots among the gray rocks. The collection can be walked around, but the plants can only be admired from the road, you must not step among them.

The species presented here have adapted to extreme growing conditions, they tolerate drought, strong wind and sunshine well. They grow well with little fertile soil, often only taking root in crevices between bare rocks. They are short, their shoots creep along the surface of the rocks or form dense cushions. Their leaves are small, often fibrous, leathery or coated with wax.
Horticultural versions of rock garden perennials, a flame flowers, that is Erika, the bluebells, the crow's feet, the bag of stone roses, the stone crusher grasses, the thymes are one of the greatest attractions of the collection.

Among the onions, wild tulips, the star flowers, the saffrons, the hoops and the snowdrops we can mention. They are only visible for a short time, they retreat into the soil after flowering and fruit ripening.

A waterfall starts at the highest rocky part, which continues in a gorge. Many ferns find their living conditions in the cool and humid microclimate of the gorge valley, giving the crevasse a wild, romantic appearance. Around the gorge, plants native to the surrounding high mountains and the Pyrenees, the Caucasus and the Balkan Mountains, dwarf pines, creeping dwarf shrubs and semi-shrubs are visible. THE dwarf pines nearly 20 horticultural varieties occur.
The back part has a close-to-nature appearance, mainly showing the species of Hungarian rock meadows and slope steppe meadows. THE sunflowers, thymes, that is Transylvanian rabbittail grass and the sweet fescue protected species can also be seen.

The rock garden also includes the ornamental rock garden that stretches along the rose garden. In autumn the Japanese anemone its pinkish, high-reaching flowers, and in spring it is wood anemone white petals bloom here en masse.
Farm yard
The most important useful and ornamental plants of the farms around Szeged and the typical atmosphere of the farm lifestyle can be seen in the farm yard.
The farm as a form of settlement played a decisive role in the Great Plain for centuries. It was not only a place to live, but also provided the families with the livelihood they needed for everyday life. All the necessary vegetables were grown in the vegetable garden around the house, the orchards provided jam and brandy, and the vineyards produced delicacies and wine grapes. Irrigation was provided by a dug well, from which water was usually drawn up by hand using a boom well. The wooded area around the house provided the necessary wood. The homesteads fit harmoniously into the landscape, the fences, outbuildings, boom box, carriages, horse tools and garden tools were typically made of wood. The walls of the residential buildings were made of adobe, and reeds or rye straw were used for roofing for a long time.
The furnishings of the fenced farmyard evoke this bygone world.

In the vegetable garden, typical vegetables grown in the Great Plain are grown every year. In the spring, spinach, radishes, peas, carrots and parsley, garlic and red onions open the row. During the year, beetroot, kale, red cabbage, cauliflower, kohlrabi, celery, broccoli, beans, food and spice peppers, and tomato varieties are also planted in the beds in the form of seeds or seedlings. By autumn, corn, sorghum, sunflowers and pumpkins will be the dominant crops. Among the fruit-bearing plants, raspberries and blackberries grow here, and you can learn about the most important fruit trees and many varieties of grapes.

Annual plants decorate the front of the fence. Among the lovely garden flowers of our grandmothers, you can see here spur, the snapdragon, the butterfly flower, the garden petunia, the purslane. The fence organ and ball rose accompanied by a bush.

The farmyard is also an important location for environmental education. Children's groups can get a taste of gardening, learn about garden tools and the plants of small gardens.
Tropical butterfly garden
The tropical butterfly garden is open periodically and can be visited from May to September. Its main attractions are the exotic butterflies native to Central and South America, which travel a long way to reach Szeged. The animals are bred on butterfly farms in Costa Rica. Pupae that arrive by air continue to develop in the butterfly garden's pupa cabinet. After 1-3 weeks, the butterflies emerge from the pupae fixed with insect needles, and in a few hours they pump up their wings with body fluid and fly into the open space of the foil tent. The environment consisting of exotic plants is their ideal habitat, where they can move freely.

Under natural conditions, butterflies feed on the nectar of flowers, so they can feed on plants that are currently blooming in the foil tent, promenade rose, the silkworm, the petunias are also visited, but they also need additional food. At the butterfly feeders, oranges, bananas and honey water await them, from which they suck the sugary solution with their tongues. Their thirst is often quenched from the moisture collected on the surface of pieces of earth and leaves. The high humidity of the air, which is provided by a wetland densely overgrown with plants and regular humidification, is important to them.
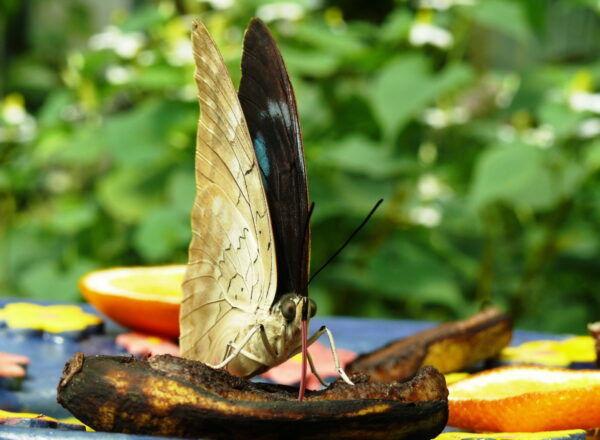

Up to a dozen butterfly species can be observed at the same time. Most of them are especially active in sunny weather, preferring to rest with folded wings on the leaves and branches of plants in darker weather.
The most spectacular inhabitants of the butterfly garden are azure butterflies. The butterflies with 10-15 cm sky-blue wings zigzag almost non-stop, they show their full beauty when they rest with their wings open.
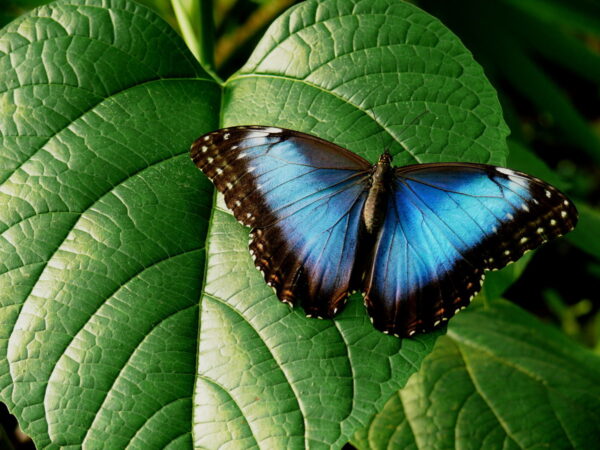

THE bat butterflies true to their name, they are more active at dusk. Apart from them, you can almost always see the malachite fox moth, the Juliet moth, the orange-spotted lady butterfly, the zebra-striped flower butterfly and numerous zebra butterfly race too.
Adult moths are short-lived, the smaller species only live for a few weeks, while the azure and bat moths live for several months.
Tropical greenhouse
In the tropical greenhouse, you can get to know plant species native to warm climates, mainly the inhabitants of rainforests and tropical plant species brought into cultivation.
The building received a completely new look in 2014. During the renovation, most of the old, 60-70-year-old plants in the space with a ceiling height of 7 meters remained in place. A staircase leads to the gallery, where you can walk around and see the collection of nearly 500 species almost from the height of the canopy.

The gallery housed the bromeliads and the philodendrons and from here you can also approach the presentation of insect-catching plants.
Among the crops a banana, the coffee, the cocoa, the vanilla, the coconut palm, the pepper, that is pineapple and the ginger can be known.

Many species of tropical rainforest plants have become popular houseplants. Decorative with their colorful bracts flamingo flowers and sail flowers next to the begonias, among leaf ornamental plants mace flower, the zebra leaf, the cancer flower and the dwarf pepper species are also represented in great variety.

Plants living in the tropics have adapted to their habitat in a variety of ways.
One of the oldest members of the collection is native to mangrove swamps Veitch screw palm obsession pandanus. The leaf stems of the nearly 70-year-old plant are supported by a thin trunk rising to a height of 6 m, from the side of which the supporting aerial roots, almost the thickness of the arm, start from the side of the plant.
Tree-dwelling plants (epiphyte-epiphyte) live in the canopy of giant trees, they settle on tree branches and forks. Their representatives can be seen here bromeliads, that is orchids and the cane cacti.
Lianas are characterized by the fact that they take root in the soil and climb up into the canopy level with their flexible stems. They include the weeping palm and that giant wolf apple.

As a result of high humidity air, some ficus species, philodendrons they develop aerial roots that sway in the air, with which they can utilize the air humidity. Perforated leaf plates and pointed leaf tips are common. These leaf modifications help the rapid drainage of rainwater.

It has palisade roots, similar to giant trees, which increase the stability of the trunk for lute-leaved ficus.
The tower behind the lake is very imposing East Indian ziggurat.




 Foundation for the Szeged Botanical Garden
Foundation for the Szeged Botanical Garden The media regularly reports on our events and developments. We collect them here…
The media regularly reports on our events and developments. We collect them here… You can read about our events by clicking on the link
You can read about our events by clicking on the link We haven't deleted our older articles either, take a look in our archive.
We haven't deleted our older articles either, take a look in our archive.